A sebaceous cyst is a common skin disorder called a deep-seated sebaceous gland or retention cyst. A sebaceous gland is found in the pores of your skin. Sebaceous glands produce oil to keep the skin moist and its natural balance of bacteria.
A sebaceous cyst is a fluid-filled sac formed by overproducing cells that line the hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and apocrine glands. These cells create a liquid layer to protect against infection and promote moisture retention.
Sebaceous cysts can be of different sizes and shapes. They can even be caused by trauma to the area. Most cysts are harmless, but occasionally they develop into a more severe condition, such as a skin infection.
If this is not treated, sebaceous cysts may rupture and become infected. This can cause permanent scarring. It also has long-term effects on how your body processes oil. There are two types of sebaceous cysts: comedonal (single) and hidden (multiple). The comedonal is the more common type of sebaceous Cyst. It will be considered a comedonal sebaceous cyst if a visible lesion is present. A hidden sebaceous cyst is sometimes related to an underlying skin disorder or disease.
What Does a Sebaceous Cyst Look Like?
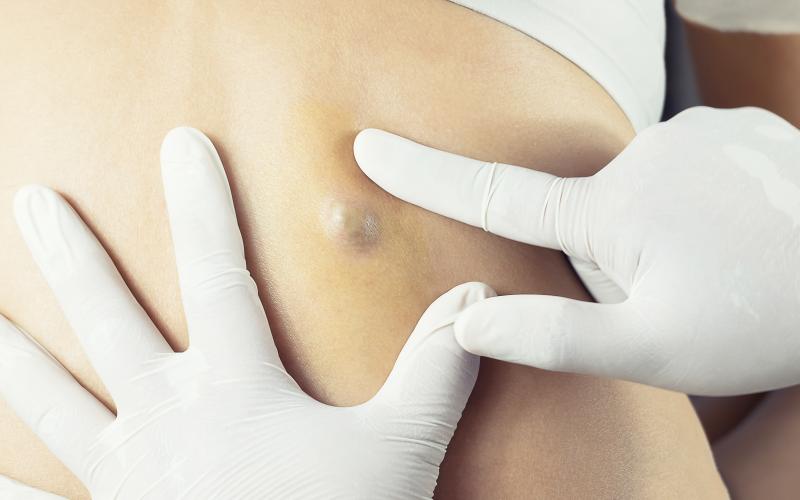
Sebaceous cysts usually develop small, round lumps on the outside of your skin. It can be hard to notice these lumps unless you know where to look. But if you squeeze the Cyst, it will have a lumpy appearance.
There are many kinds of sebaceous cysts, and not all of them will have the same appearance. They can be white or yellowish, or even black. Some may be very small, while others can be bigger than a half-dollar. The size of a sebaceous cyst depends on the type of fluid it contains. Most cystic lesions contain clear fluid. Others may contain pink, green, or semisolid material.
Some have a rigid, rubbery feel, while others feel like they have a soft, liquid consistency.
The location of the sebaceous Cyst is also an essential factor in how it will look, and it sometimes determines how long it will take to develop. Sebaceous cysts usually occur in the face, neck, scalp, ears, eyelids, etc. Depending on where it is located, you may see a small bump or feel a small lump under the skin.
What Causes a Sebaceous Cyst
An overproduction of cells usually causes sebaceous cysts. Typically, the sebaceous gland produces a protective oil released when the hair follicle is active. However, sometimes these glands become blocked for various reasons, and the secretion builds up inside without being released. The liquid layer eventually becomes a mass of cells. This causes the sebaceous Cyst.
This natural draining process slows down as you get older, and you are more likely to develop sebaceous cysts on your skin. The most common reasons for developing sebaceous cysts are:
- a break in the follicle wall
- an injury to the area
- acne or a previously infected acne cyst
- infection, especially with the staphylococcus bacteria
These factors may contribute to developing sebaceous cysts. Other factors that may contribute are genetics and exposure to toxins.
Proper Treatment Methods
You can treat the Cyst with medicine, surgery, or inject liquid or air into the Cyst. The best treatment depends on whether the Cyst is located on your skin surface or deep inside your body.
The most common treatment for sebaceous cysts is pharmaceutical medicine. It is usually used to help rid the body of the Cyst, such as by draining it or eliminating the liquid inside. The medicine dissolves the Cyst, destroys its contents, and eliminates the physical symptoms.
In some cases, surgery can be performed to eliminate or drain a sebaceous cyst. This is called a surgical excision or an incisional procedure. It involves taking a small amount of tissue from the Cyst. Then the removed tissue is sent to be tested for infectious diseases, such as staphylococcus bacteria. If any signs of infection are found, you will be treated accordingly.
If the Cyst is located deep under the skin and very difficult to see, medications can be injected into the Cyst. This is called a percutaneous injection: a needle is used to break up and release the fluid structure of the Cyst. Any liquid can be injected, including cream or serum, that will allow your body to absorb it later.